Surgical table accessories enhance operating table functionality, ensuring patient safety, precise positioning, and procedural efficiency. These tools allow customization for specific surgeries, reducing risks like pressure injuries and improving surgical site access. Used by surgeons across specialties, this guide covers key accessory types, their subtypes, uses, procedures, quality factors, compatibility, materials, terminology, and alternative names you may encounter.
Shop Surgical Table Accessory Options 🛒
Ensuring Accessory Compatibility with Your Surgical Table
- Side Rail Compatibility:
- Check Rail Dimensions: Most accessories (e.g., arm boards, clamps, IV poles) attach to side rails. Verify your table’s rail size, typically 1 x 0.4 inches (standard US rails) or similar (e.g., 25×10 mm for EUR rails). Ensure clamps or hooks match these dimensions.
- Example: Infinium Medical’s Square Siderail Clamp fits standard US rails (1 x 0.4 inches).
- Attachment Mechanism:
- Confirm Clamp/Hook Type: Accessories use clamps (e.g., Clark socket, square siderail), hooks, or docking systems. Check if your table supports quick-release clamps, gear devices, or specific sockets (e.g., for waste trays or head stabilizers).
- Example: Anesthesia Screen requires sturdy clamps for universal rail attachment.
- Table Model Compatibility:
- Verify Manufacturer Specifications: Tables like Allen, Jackson, or Infinium models (e.g., ST500) have specific accessory compatibility. Consult the table’s manual or manufacturer (e.g., Infinium Medical’s product range) to confirm fit for modular or standalone accessories like Jackson spine frames.
- Weight and Load Capacity:
- Match Patient Weight Limits: Ensure accessories support your table’s weight capacity (e.g., 500 lbs for beach chairs, 350 lbs for leg holders). Overloading can cause instability or damage.
- Example: Beach Chair Module supports up to 500 lbs for shoulder procedures.
- Positioning and Adjustment Range:
- Ensure Positional Fit: Accessories like arm boards or traction frames must align with your table’s positioning capabilities (e.g., Trendelenburg, lateral tilt). Check adjustment ranges (e.g., 0-90° for beach chairs) to match table articulation.
- Example: Hana Table Traction Frame requires abductor bar compatibility.
- Modular vs. Standalone Fit:
- Check Integration Type: Some accessories (e.g., spinal frames, beach chairs) are modular and attach to specific table sections (head, foot), while others (e.g., Jackson spine table) are standalone. Verify if your table supports modular attachments or requires dedicated systems.
- Sterilization and Material Compatibility:
- Confirm Cleaning Protocols: Accessories (e.g., stainless steel waste trays, gel pads) must align with your table’s sterilization methods (e.g., autoclaving). Ensure materials like stainless steel or carbon fiber withstand your OR’s cleaning standards.
- Example: Gel Prone Horseshoe Headrest uses anti-microbial gel for easy cleaning.
- FDA and Safety Standards:
- Verify Regulatory Compliance: Ensure accessories meet FDA regulations for medical devices and are from distributors or manufacturers that observe FDA, CE, & MDR standards, especially for critical components like head stabilizers. Check for certifications to avoid compatibility or safety issues.
- Example: Mayfield Style Head Stabilizer ensures secure fixation for craniotomies.
Table Brand Fitting Considerations
Common Types of Surgical Table Accessories
Surgical table accessories are vital tools that customize operating tables for specific procedures, enhancing patient safety, comfort, and surgical precision. From arm boards and clamps to specialized traction frames and waste trays, these accessories cater to diverse surgical needs, including orthopedic, neurosurgical, and urological procedures. Available in various subtypes, such as articulating arm boards or Mayfield-style head stabilizers, they ensure compatibility with standard tables while addressing unique positioning requirements. The following guide details key accessory types, their subtypes, uses, and compatibility factors to help you select the right equipment for your operating room.

Arm Boards
Arm boards are padded, adjustable extensions attached to surgical table side rails to support and position a patient’s arms, preventing nerve damage and ensuring optimal surgical access.
- Subtypes:
- Hand Microsurgery Arm Board: Adjustable for fine hand procedures (e.g., Hand Microsurgery Arm Board).
- Hanging Universal Arm Board: Suspended design for versatile positioning.
- Lateral Position Arm Board: Curved for side-lying stability.
- Standard Surgical Arm Board: General-purpose with supine padding.
- Vertical Three Joint Arm Board: Multi-joint for complex angles.
- Who Uses Them: General and orthopedic surgeons, anesthesiologists.
- Procedures: Abdominal, shoulder arthroscopy, hand microsurgery.
- Quality Factors: Radiolucent materials, padded surfaces, quick-release clamps, 100+ lbs capacity.
- Fit: Clamp to standard side rails (1 x 0.4 inches); fits Allen, Jackson tables.
- Materials: Carbon fiber, stainless steel, foam/gel padding.
- Terms: Radiolucent (X-ray transparent), Articulating (multi-joint).
- Other Names: Arm rests, shields, articulating armboards.

Anesthesia Screens
Anesthesia screens are metal frames or drapes that create a sterile barrier between the patient’s head and the surgical field, allowing anesthesiologists to manage airways while maintaining a clean operative area.
- Who Uses Them: Anesthesiologists, surgical teams.
- Procedures: General, orthopedic, neurosurgery (e.g., Anesthesia Screen).
- Quality Factors: Adjustable height/angle, sturdy clamps, drape compatibility.
- Fit: Clamps to side rails; universal fit.
- Materials: Stainless steel, aluminum.
- Terms: Sterile Field (contaminant-free surgical area).
- Other Names: Anesthetic frames/screens.
Beach Chairs
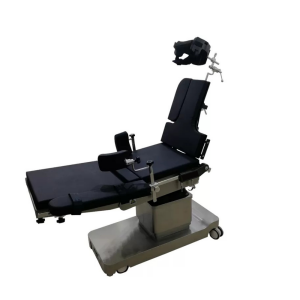
Beach chairs are specialized positioning modules that elevate the patient’s upper body into a semi-upright “beach chair” position, with integrated head and arm supports for enhanced stability during shoulder procedures.
- Who Uses Them: Orthopedic shoulder surgeons.
- Procedures: Shoulder arthroscopy, rotator cuff repairs (e.g., Beach Chair Module).
- Quality Factors: Padded, 0-90° adjustable, 500 lbs capacity, traction-compatible.
- Fit: Attaches to head section via clamps/docks.
- Materials: Foam padding, carbon fiber.
- Terms: Fowler’s Position (semi-upright).
- Other Names: Shoulder chairs/positioners.

Clamps
Clamps are robust attachment devices that secure various accessories, such as arm boards or screens, to the surgical table’s side rails, ensuring stability during procedures.
- Subtypes:
- Round Clark Socket Clamp: Circular clamp for secure, non-rotating hold.
- Square Siderail Clamp: Fits standard US rails for versatile accessory attachment (e.g., Square Siderail Clamp).
- Who Uses Them: Surgical teams.
- Procedures: All accessory-dependent surgeries.
- Quality Factors: Quick-release, rail compatibility (US/UK), non-rotatable.
- Fit: Standard rails (1 x 0.4 inches); universal options.
- Materials: Stainless steel.
- Terms: Clark Socket (round clamp).
- Other Names: Side rail/accessory clamps.

Foot Boards
Foot boards are padded platforms or supports designed to stabilize and position a patient’s feet and knees, preventing foot drop and ensuring proper alignment during lower extremity procedures.
- Who Uses Them: Orthopedic, general surgeons.
- Procedures: Knee replacements, lithotomy positions (e.g., Foot Boards).
- Quality Factors: Adjustable height, non-slip, padded.
- Fit: Foot section or rails.
- Materials: Aluminum, steel, foam.
- Terms: Lithotomy Position (legs elevated/apart).
- Other Names: Knee boards, foot rests.

Surgical Positioning Pads
Positioning pads are viscoelastic gel cushions placed under body parts to distribute pressure evenly, preventing ulcers and ensuring patient comfort during extended surgeries.
- Subtypes:
- Wilson Frame Gel Pad: Supports intervertebral disc procedures.
- Abdominal & Chest Roll: For prone positioning.
- Contoured Arm Tucking Pad: Secures arms in femoral condyle positioning.
- Horseshoe Headrest: Open design for prone head support (e.g., Gel Prone Horseshoe Headrest).
- Square Headrest: Prone head support with solid design.
- Closed Head Ring: Supine head positioning.
- Knee, Leg, Ankle Pad: General lower extremity support.
- Lateral Position Pad: Side-lying support.
- Prone Chest & Pelvic Pad: Chest/pelvis support in prone position.
- Rounded Multi-Position Pad: General surgery positioning.
- Procedures: Most procedures including Spine (prone), and hip (lateral) surgeries.
- Quality Factors: Anti-microbial gel, reusable/disposable, thickness and durability of casing material.
- Fit: Placed on table/frames.
- Materials: Viscoelastic gel.
- Terms to know: Decubitus Ulcer (pressure sore).
- Other Names: Gel positioners, pressure relief pads.
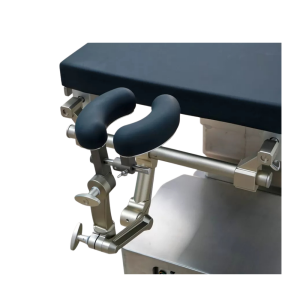
Head Stabilizers
Head stabilizers, such as Mayfield clamps or gel headrests, are devices that securely immobilize the patient’s head to ensure precision and safety during cranial or spinal procedures.
- Subtypes:
- Carbon Fiber Prone Head Stabilizer: Radiolucent for imaging.
- Mayfield Style Head Stabilizer: Three-point fixation for craniocerebral procedures (e.g., Mayfield Style Head Stabilizer).
- Who Uses Them: Neurosurgeons, ENT specialists.
- Procedures: Craniotomies, spinal surgeries.
- Quality Factors: Radiolucent, adjustable pins, padded.
- Fit: Clamp to rails or frames.
- Materials: Carbon fiber, stainless steel.
- Terms: Three-Point Fixation (skull pins).
- Other Names: Skull clamps, craniocerebral frames.
IV Poles
IV poles are adjustable poles attached to the surgical table for hanging intravenous fluid bags, ensuring easy access for fluid or medication administration.
- Who Uses Them: Anesthesiologists.
- Procedures: Any requiring fluids/medications.
- Quality Factors: Height-adjustable, stable, multiple hooks.
- Fit: Clamp to side rails.
- Materials: Stainless steel.
- Terms: N/A.
- Other Names: Infusion stands.
Jackson Spine Tables/Frames
Jackson spine tables or frames are specialized structures for prone spinal positioning, with open abdominal access to reduce pressure and enhance imaging clarity.
- Subtypes:
- Jackson Spine Table: Standalone table for spinal procedures.
- Carbon Fiber Spinal Frame: Modular frame for imaging.
- Carbon Wilson Spine Frame: Wilson-style for specific spinal support.
- Who Uses Them: Neurosurgeons, spine specialists.
- Procedures: Spinal fusions, decompressions.
- Quality Factors: Carbon fiber, adjustable bows for lordosis.
- Fit: Standalone or modular.
- Materials: Carbon fiber composites.
- Terms: Lordosis (spinal curvature).
- Other Names: Wilson frames, docking tables.

Lateral Supports
Lateral supports are padded braces that stabilize patients in side-lying positions, ensuring secure positioning during lateral procedures.
- Subtypes:
- Light Upper Body & Lumbar Supports: Lightweight for lumbar focus.
- Universal Orthopedic & Neurosurgical Supports: Broad application (e.g., Universal Lateral Support).
- Waist & Pelvic Supports: Focused on pelvic stabilization.
- Who Uses Them: Orthopedic, general surgeons.
- Procedures: Hip replacements, kidney surgeries.
- Quality Factors: Curved cushions, angular adjustments.
- Fit: Clamp to rails with gear devices.
- Materials: Foam, steel.
- Terms: Lateral Decubitus (side-lying).
- Other Names: Body supports, pelvic fixators.

Leg Holders/Stirrups
Leg holders or stirrups are devices, such as candy cane or pneumatic models, that elevate and separate legs for optimal positioning during lower body procedures.
- Subtypes:
- Arthroscopic Total Knee Support: For knee arthroscopy.
- General Use Knee Support: Broad lower extremity use.
- Large General Surgery Leg Holder: For larger patients.
- Blue Pneumatic Lithotomy Stirrups: Pneumatic for ease (e.g., Blue Pneumatic Stirrups).
- Yellow Cystoscopy/Candy Cane Stirrups: Lightweight for urology.
- Who Uses Them: Gynecologists, urologists, orthopedic surgeons.
- Procedures: Cystoscopy, knee arthroscopy.
- Quality Factors: Pneumatic assist, 350 lbs capacity, padded boots.
- Fit: Clamp to rails; traction options.
- Materials: Stainless steel, foam.
- Terms: Arthroscopic (minimally invasive joint surgery).
- Other Names: Legholders, lithotomy stirrups.

Ophthalmic Hand Frames
Ophthalmic hand frames are U-shaped supports that stabilize surgeons’ hands during delicate eye surgeries, ensuring precision and reducing fatigue.
- Who Uses Them: Ophthalmologists.
- Procedures: Cataract, retinal surgeries.
- Quality Factors: Adjustable height, stable.
- Fit: Clamp to head section.
- Materials: Stainless steel.
- Terms: N/A.
- Other Names: Wrist rests, hand supports.
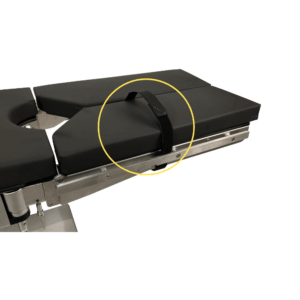
Restraint Straps
Restraint straps are padded, adjustable straps that secure patients to the table during tilting, preventing movement and ensuring safety.
- Subtypes:
- Arm Straps (Set of 2): For arm immobilization.
- Forearm Restraint Strap: Single forearm strap.
- Head Restraint Strap: For head stabilization.
- Leather Body Safety Belt: Full-body restraint (e.g., Leather Body Safety Belt).
- Leg Restraint Strap: For leg immobilization.
- Safety Belt: General-purpose restraint.
- Procedures: Trendelenburg positions.
- Quality Factors: Velcro, soft padding, adjustable.
- Fit: Loop around rails/body.
- Materials: Leather, nylon.
- Terms: Trendelenburg (head-down tilt).
- Other Names: Safety belts, body restraints.

Traction Frames
Traction frames are structures that apply controlled pulling force to limbs or the spine, aiding in alignment during orthopedic procedures.
- Subtypes:
- Shoulder Traction Frame: Lightweight for shoulder procedures.
- Carbon Fiber Orthopedic Traction Frame: Mixed materials for durability.
- Hana Table Traction Frame: Orthopedic-specific design (e.g., Hana Table Traction Frame).
- Who Uses Them: Orthopedic surgeons.
- Procedures: Hip fractures, spinal alignments.
- Quality Factors: Carbon fiber, adjustable traction.
- Fit: Attach to abductor bars.
- Materials: Carbon fiber, stainless.
- Terms: Traction (pulling force).
- Other Names: Hana, lower limb frames.
Waste Trays
Waste trays are reusable stainless steel platforms or attachments that mount to the surgical table’s end or side rails to contain fluids, waste materials, and small instruments, promoting a clean and organized operative environment during procedures.
- Who Uses Them: Surgeons in fluid-heavy procedures.
- Procedures: Urology, bariatric surgeries, general OR waste management.
- Quality Factors: Secure clamps, removable trays (e.g., 12 x 19 inches), corrosion-resistant for autoclaving; optional disposable liners for single-use fluid collection.
- Fit: Seat section or side rail attachment via sockets or hooks.
- Materials: Stainless steel (primary for reusability); disposable plastic liners/bags for fluid containment.
- Terms: Autoclavable (sterilizable via steam).
- Other Names: Mayo trays, drainage trays, fluid collection pans.
Surgical Table Accessory Additional Resources
- AORN Guidelines for Positioning: Standards for safe patient positioning.
- NCBI: Patient Positioning: Review of positioning techniques.
- ASA Safety Resources: Anesthesia equipment guidelines.
Always choose surgical table accessories based on procedure needs, table compatibility (e.g., Infinium Medical’s range), and quality features like radiolucency and durability. Ensure FDA / CE / EU MDR are address with any distributor or source manufacturer for compliance and safety.